🧠 Mastering RAG: Empowering AI Models with Our Custom Data
Most Large Language AI models, such as ChatGPT (Generative Pre-Trained Transformer), are pre-trained on vast datasets containing billions of examples. When users request specific information, these AI models leverage their pre-trained knowledge to generate responses. However, this approach has limitations—responses may contain outdated information since the training data has a fixed cutoff date.
Introduction
Most Large Language AI models, such as ChatGPT (Generative Pre-Trained Transformer), are pre-trained on vast datasets containing billions of examples. When users request specific information, these AI models leverage their pre-trained knowledge to generate responses. However, this approach has limitations—responses may contain outdated information since the training data has a fixed cutoff date.
In today’s fast-paced world, we need AI models that can provide accurate, up-to-date information and work seamlessly with our proprietary data sources.
Enabling AI Models to Work with Custom Data
There are several sophisticated techniques to integrate custom data with AI models:
Fine-Tuning
This involves retraining the model on specific datasets to specialize its knowledge for particular domains or use cases.
Prompt Augmentation
This technique involves enriching user prompts with relevant custom data, ensuring the AI model has the necessary context to generate accurate, domain-specific responses. This approach is often called “prompt stuffing” or context injection.
Rather than manually adding content to every prompt, we employ an advanced technique called RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation), which automatically enhances prompts with relevant information from your knowledge base.
Understanding RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation)
RAG is a powerful three-stage process that bridges the gap between pre-trained AI models and your custom data:
🔍 R - Retrieval
Intelligently searches through your knowledge base (documents, databases, web content) to identify information most relevant to the user’s query.
🔗 A - Augmented
Seamlessly combines the original user prompt with the retrieved contextual information, creating a comprehensive, enriched prompt that provides the AI model with all necessary background knowledge.
✨ G - Generation
The AI model processes the augmented prompt to generate accurate, contextually relevant responses based on your specific data.
Core Concepts: Embeddings and Vectors
Before diving deeper into RAG implementation, it’s essential to understand two fundamental concepts:
🔗 🚀 Complete Guide to Vectors and TF-IDF in RAG Systems
Embeddings
Embeddings are sophisticated numerical representations that capture the semantic meaning of text, images, or audio content. These high-dimensional arrays of floating-point numbers encode relationships and similarities between different pieces of content, enabling machines to understand context and meaning in ways similar to human comprehension.
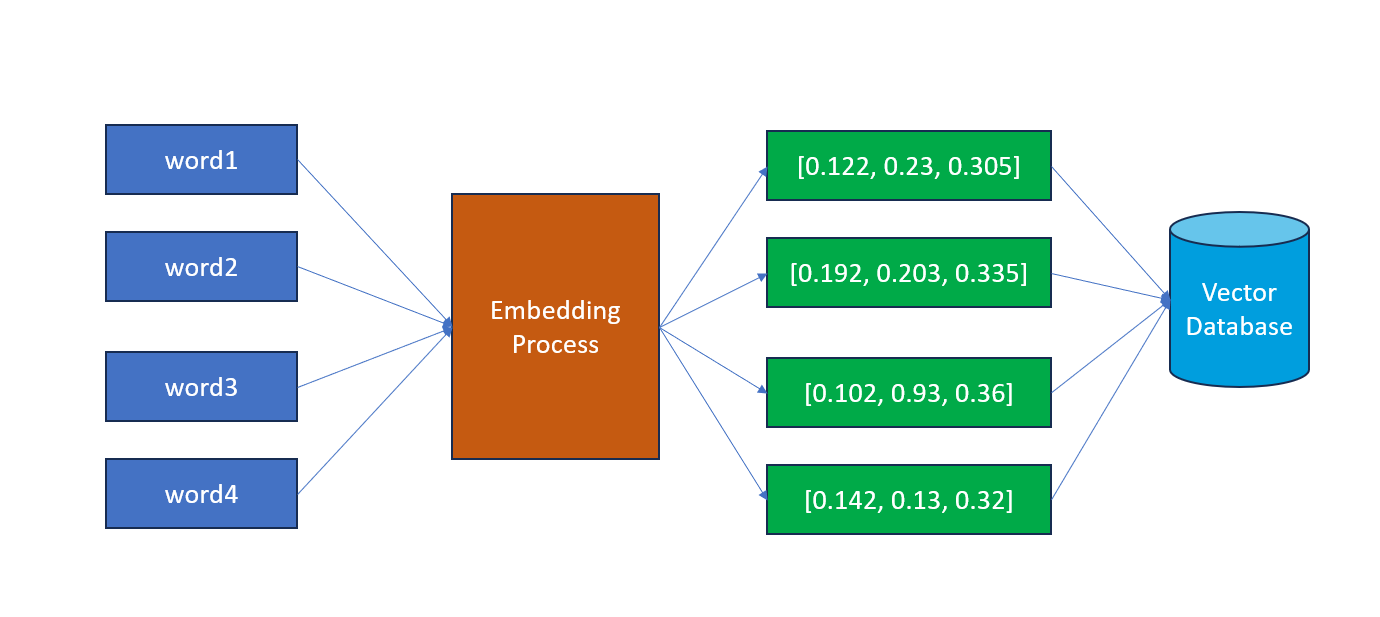
Vectors
When embeddings are generated, they create arrays of floating-point numbers called vectors. Each vector has a specific dimension (length), typically ranging from hundreds to thousands of elements. The mathematical distance between vectors indicates semantic similarity—closer vectors represent more related content.
Key Insight: RAG leverages these vector relationships to identify and retrieve the most relevant information for any given query.
RAG Implementation: A Two-Phase Approach
Implementing RAG involves two distinct phases that work together to create a powerful, data-aware AI system:
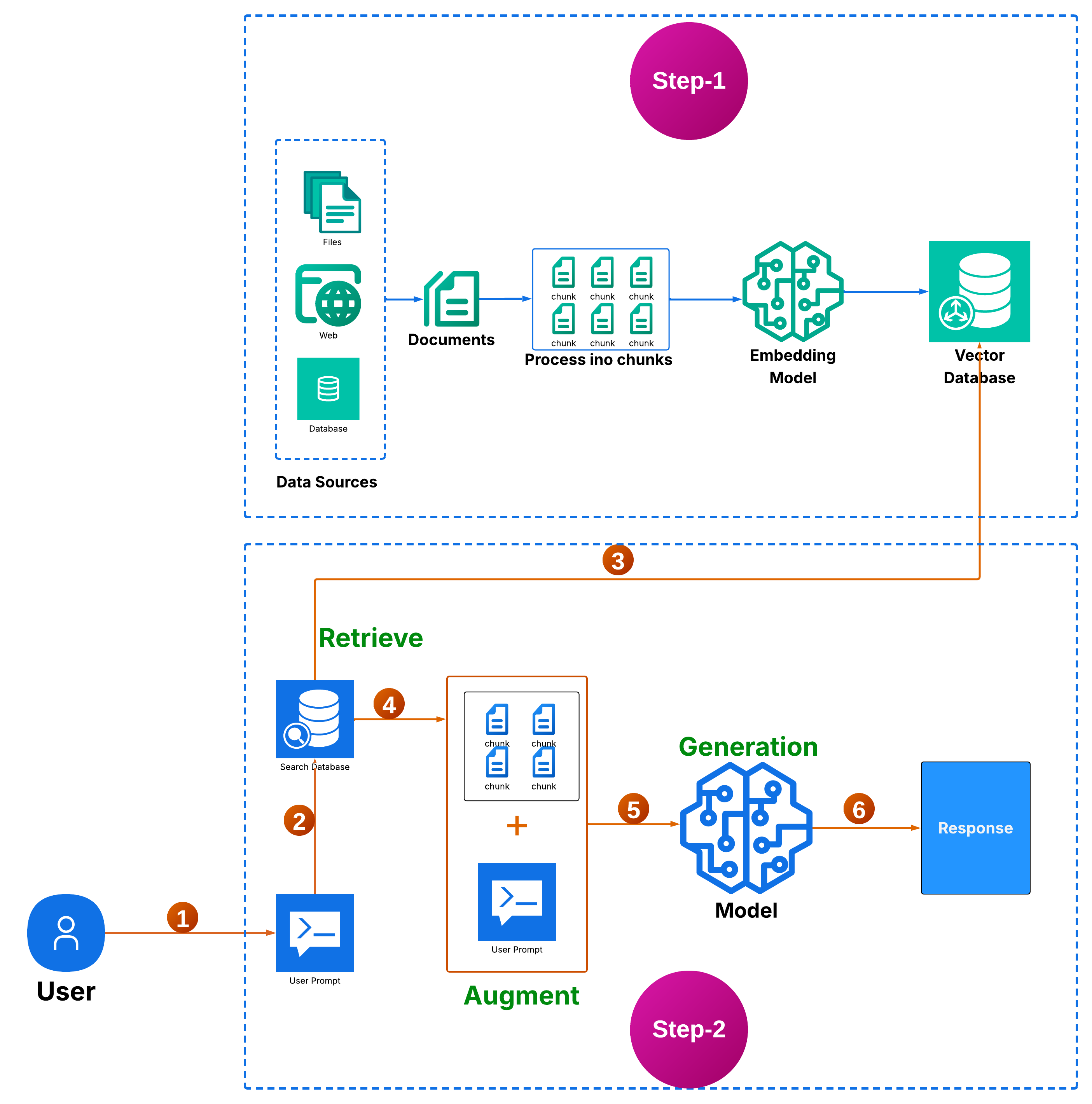
Phase 1: Knowledge Base Preparation
📊 Data Source Identification
Begin by cataloging all relevant data sources, including:
- Document repositories (PDFs, Word files, presentations)
- Web content and articles
- Database records and structured data
- Internal knowledge bases and wikis
📝 Document Processing
Transform raw data into structured, meaningful documents that can be effectively processed by AI systems. This involves cleaning, formatting, and organizing content for optimal retrieval.
✂️ Content Chunking
Break down large documents into smaller, semantically meaningful segments (chunks). Each chunk should:
- Contain complete thoughts or concepts
- Maintain context independence
- Be appropriately sized for embedding generation (typically 100-500 tokens)
🧠 Vector Generation
Utilize specialized AI embedding models (such as OpenAI’s text-embedding-ada-002 or similar) to convert text chunks into high-dimensional vectors. Alternative approaches include:
- Open-source embedding libraries
- Custom-trained embedding models
- Domain-specific embedding solutions
💾 Vector Storage
Store generated vectors in specialized vector databases optimized for similarity search, such as:
- Cloud Solutions: Pinecone, Weaviate, Qdrant
- Self-Hosted Options: Chroma, FAISS, Milvus
- Simple Alternatives: Local filesystem storage with similarity search libraries
Phase 2: RAG-Enhanced Query Processing
🎯 Retrieval Phase
When a user submits a query:
- Convert the query into a vector using the same embedding model
- Perform similarity search against the vector database
- Retrieve the most relevant content chunks based on vector proximity
- Rank and filter results based on relevance scores
🔄 Augmentation Phase
Intelligently combine retrieved information with the original user query:
- Merge relevant context seamlessly
- Maintain query intent and focus
- Structure information for optimal AI processing
- Ensure prompt length stays within model limits
🚀 Generation Phase
Submit the enriched prompt to your chosen AI model, which now has access to:
- The original user question
- Relevant context from your knowledge base
- Sufficient background information for accurate responses
Benefits of RAG Implementation
- 🎯 Accuracy: Responses grounded in your specific data sources
- ⚡ Real-time: Access to current information without model retraining
- 🔧 Flexibility: Easy to update knowledge base without technical complexity
- 💰 Cost-Effective: No expensive model fine-tuning required
- 🔒 Privacy: Keep sensitive data within your infrastructure
Conclusion
RAG represents a paradigm shift in how AI models interact with custom data, offering a practical, scalable solution for organizations seeking to leverage AI while maintaining control over their information assets. By implementing RAG, you transform static AI models into dynamic, knowledge-aware assistants that provide accurate, contextual responses based on your unique data landscape.
