🚀 Embedding Models: Powering Intelligent RAG Systems with Vector Generation
Embedding models are AI models used to generate arrays of embeddings called vectors for given input text. These models provide a more convenient way to generate embeddings or vectors compared to traditional methods, making the RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) process simpler and more efficient.
📋 Overview
Embedding models are AI models used to generate arrays of embeddings called vectors for given input text. These models provide a more convenient way to generate embeddings or vectors compared to traditional methods, making the RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) process simpler and more efficient.
📚 Related Resources
🧠 What Are Embedding Models?
Embedding models transform text into numerical representations (vectors) that capture semantic meaning. Unlike traditional approaches such as TF-IDF, embedding models can:
- 🔗 Understand context and semantic relationships
- 🎯 Generate dense vector representations
- 🎭 Capture nuanced meanings in text
- 🔍 Provide better similarity matching
🔄 Role in RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation)
🛠️ Knowledge Base Preparation
As part of the RAG pipeline, embedding models play a crucial role in preparing the knowledge base:
- 📊 Data Collection: Gather information from various data sources including:
- 📄 Files (PDFs, documents, etc.)
- 🌐 Web content
- 🗄️ Databases
- 📁 Other structured/unstructured data
-
🎯 Vector Database Creation: Use embedding models to convert text into vectors and store them in a vector database
- 🔍 Semantic Search: Enable efficient retrieval of relevant information based on semantic similarity
⚡ RAG Process Enhancement
Once the vector database is established, it serves as the foundation for generating more accurate chat responses:
- 💬 Query Processing: Convert user queries into vectors using the same embedding model
- 🔎 Similarity Search: Find the most relevant content from the knowledge base
- 📈 Context Enhancement: Provide relevant context to the language model for better response generation
⚖️ Traditional vs. Embedding Model Approaches
📊 TF-IDF Approach
- 📐 Based on term frequency and inverse document frequency
- 🔤 Limited to exact word matches
- ❌ Doesn’t capture semantic meaning
- 🔎 Suitable for simple keyword-based searches
🧠 Embedding Models
- 🔗 Capture semantic relationships
- 📝 Handle synonyms and related concepts
- 🎯 Provide dense vector representations
- 🤖 Better for complex query understanding
🎭 Demonstration Setup with Ollama
For practical implementation, this guide uses Ollama local embedding models to generate embeddings. This approach offers:
- 💻 Local Processing: No need for external API calls
- 🔒 Privacy: Data stays on your local machine
- 💰 Cost Efficiency: No per-request charges
- ⚙️ Customization: Ability to fine-tune for specific use cases
🛠️ Available Ollama Embedding Models
Browse the complete list of embedding models at: https://ollama.com/search?c=embedding
Popular embedding models include:
| Model | Parameter Size | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 🚀 mxbai-embed-large | 334M | High-performance embedding model |
| ⚖️ nomic-embed-text | 137M | Balanced performance and efficiency |
| 💨 all-minilm | 23M | Lightweight model for basic tasks |
⚙️ Installation and Setup
✅ Prerequisites
- 🔧 Install Ollama and Start Ollama local model
- Follow the guide: Ollama Local AI Model Platform
- 📥 Pull Embedding model:
ollama pull mxbai-embed-large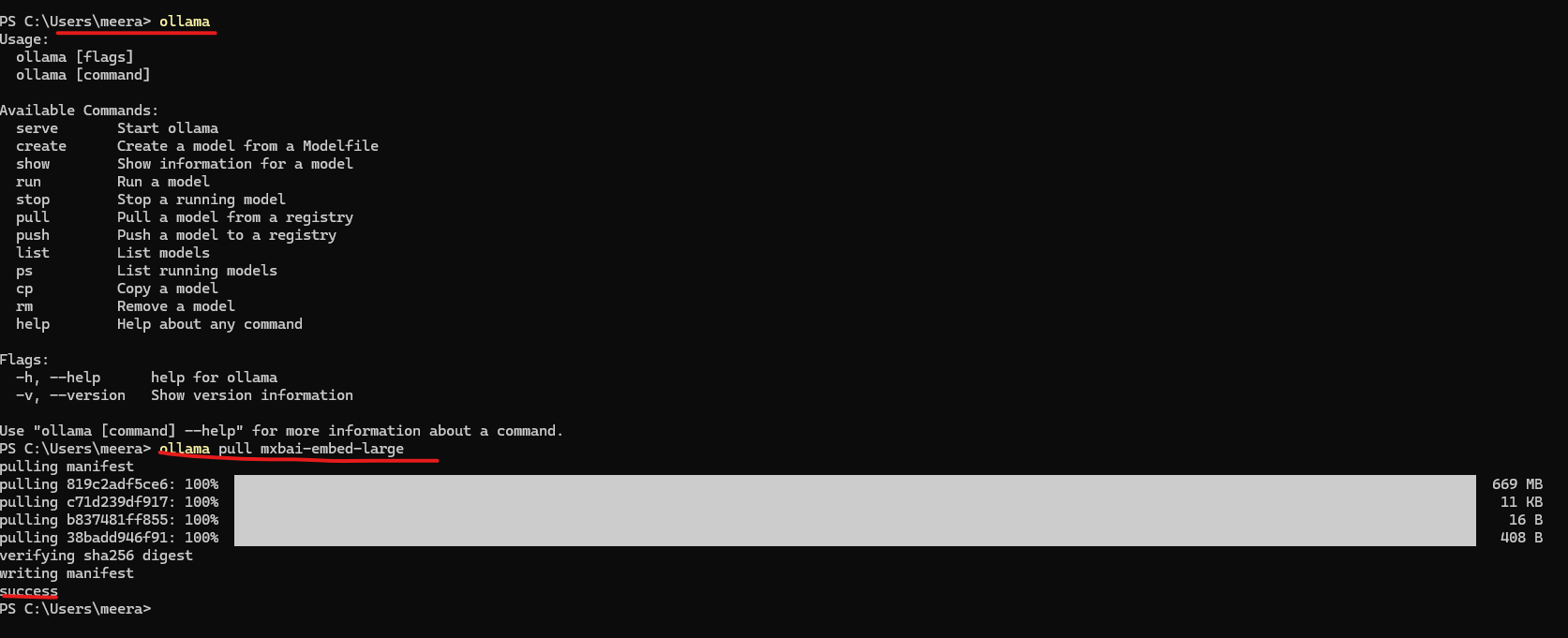
- 📦 Install required Python packages:
pip install ollama chromadb
🎯 Generating Embeddings
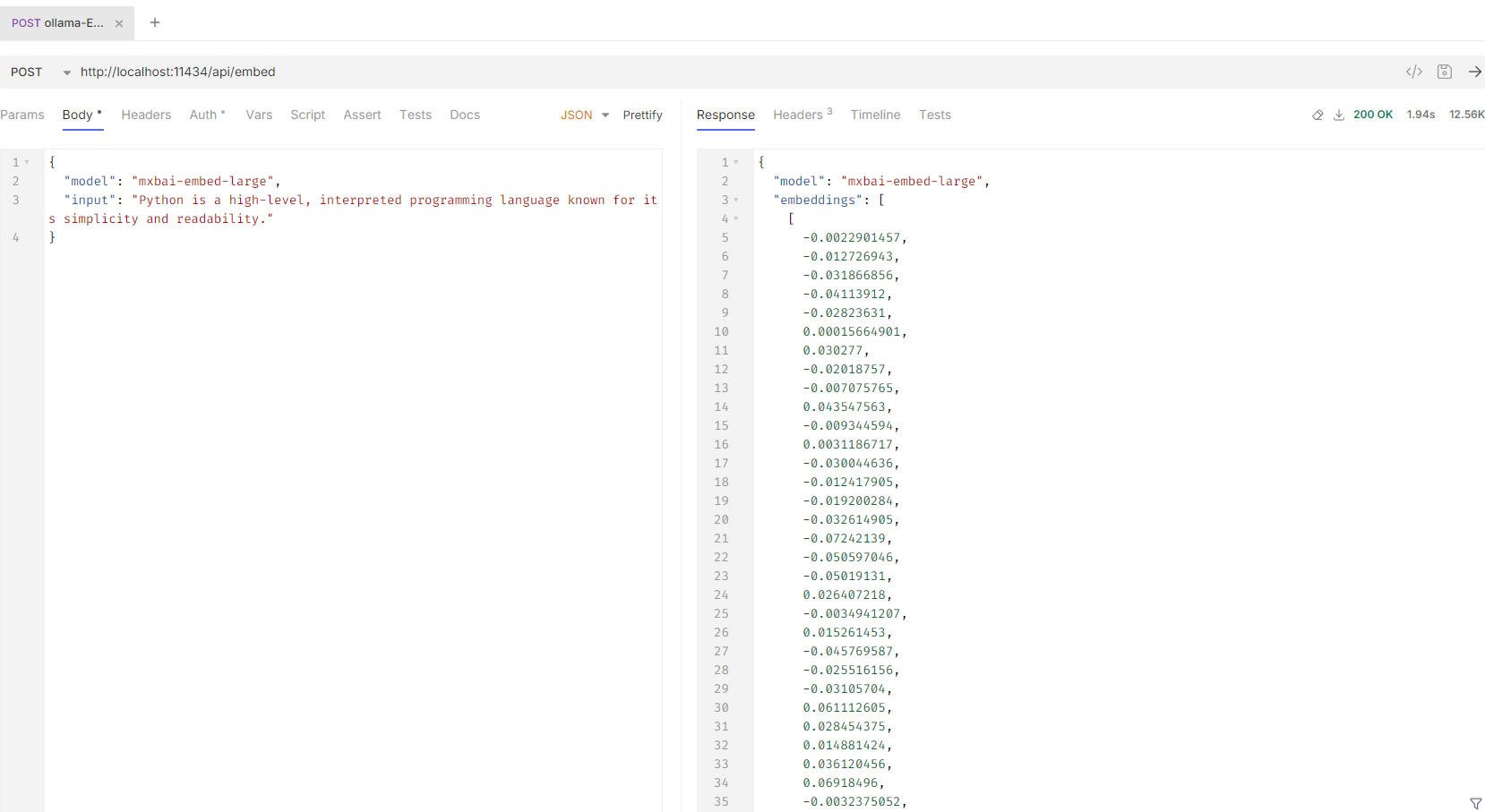
🌐 Using REST API
curl --request POST \
--url http://localhost:11434/api/embed \
--header 'content-type: application/json' \
--data '{
"model": "mxbai-embed-large",
"input": "Python is a high-level, interpreted programming language known for its simplicity and readability."
}'
🐍 Using Python Library
ollama.embed(
model='mxbai-embed-large',
input='Python is a high-level, interpreted programming language known for its simplicity and readability.',
)
🔄 How RAG Works with Embeddings to Generate More Accurate Chat Responses
Let’s understand how embeddings are created for given text and how RAG works to generate more accurate chat responses from a knowledge base.
🧪 Example Implementation
Assume we have the following document that we’ll use with embedding models to generate vectors, storing them in a Chroma vector database. Chroma is an open-source database designed to store embeddings efficiently.
📄 Sample Content
"Python is a high-level, interpreted programming language known for its simplicity and readability. Java is a widely used, object-oriented programming language and computing platform first released in 1995. Java and Python are both popular, high-level programming languages, but they have different strengths and weaknesses."
📦 Document Chunking
First, convert the document into chunks - a collection of documents called a corpus:
documents = [
"Python is a high-level, interpreted programming language known for its simplicity and readability.",
"Java is a widely used, object-oriented programming language and computing platform first released in 1995.",
"Java and Python are both popular, high-level programming languages, but they have different strengths and weaknesses."
]
🗄️ Generate Embeddings and Store in Vector Database
This process is called preparing the knowledge base. We use embedding models to generate the embeddings and store them in a vector database. ChromaDB is an open-source vector database.
# Initialize ChromaDB client and create collection
client = chromadb.Client()
collection = client.create_collection(name="docs")
documents = [
"Python is a high-level, interpreted programming language known for its simplicity and readability.",
"Java is a widely used, object-oriented programming language and computing platform first released in 1995.",
"Java and Python are both popular, high-level programming languages, but they have different strengths and weaknesses."
]
# Store each document in a vector embedding database
for i, d in enumerate(documents):
print(f" Processing document {i+1}: {d[:50]}...")
response = ollama.embed(model="mxbai-embed-large", input=d)
# Extract the first (and only) embedding from the response
embeddings = response["embeddings"][0]
collection.add(
ids=[str(i)],
embeddings=[embeddings],
documents=[d]
)
🔄 RAG Process
🔍 Retrieve
In the retrieval phase, we will use the user prompt to get the most relevant document:
prompt = "What is python?"
response = ollama.embed(
model="mxbai-embed-large",
input=prompt
)
# Extract the first embedding and pass it correctly
query_embedding = response["embeddings"][0]
results = collection.query(
query_embeddings=[query_embedding],
n_results=1
)
# Get the most relevant document
data = results['documents'][0][0]
⚡ Augmentation and Generate
This phase combines the user prompt with contextual data generated as part of the retrieval phase, and this is called prompt stuffing. Finally, we use an AI model to generate an accurate response from our knowledge base. This way, AI models use our data to generate the most up-to-date and accurate chat response based on the user prompt.
# Generate a response combining the prompt and data we retrieved
output = ollama.generate(
model="llama3.2",
prompt=f"Using this data: {data}. Respond to this prompt: {prompt}"
)
💻 Complete Code Example
# embedding-model.py
import ollama
import chromadb
# ANSI color codes for terminal formatting
class Colors:
HEADER = '\033[95m' # Magenta
BLUE = '\033[94m' # Blue
CYAN = '\033[96m' # Cyan
GREEN = '\033[92m' # Green
YELLOW = '\033[93m' # Yellow
RED = '\033[91m' # Red
BOLD = '\033[1m' # Bold
UNDERLINE = '\033[4m' # Underline
END = '\033[0m' # Reset to default
# Sample documents for the knowledge base
documents = [
"Python is a high-level, interpreted programming language known for its simplicity and readability.",
"Java is a widely used, object-oriented programming language and computing platform first released in 1995.",
"Java and Python are both popular, high-level programming languages, but they have different strengths and weaknesses."
]
print(Colors.BOLD + Colors.HEADER + "=" * 80)
print("AICodeGeek🚀 RAG SYSTEM - RETRIEVAL AUGMENTED GENERATION")
print("=" * 80 + Colors.END)
# Initialize ChromaDB client and create collection
client = chromadb.Client()
collection = client.create_collection(name="docs")
print(f"\n{Colors.BLUE}📚 Building Knowledge Base...{Colors.END}")
print(Colors.BLUE + "-" * 40 + Colors.END)
# Store each document in a vector embedding database
for i, d in enumerate(documents):
print(f" Processing document {i+1}: {d[:50]}...")
response = ollama.embed(model="mxbai-embed-large", input=d)
# Extract the first (and only) embedding from the response
embeddings = response["embeddings"][0]
collection.add(
ids=[str(i)],
embeddings=[embeddings],
documents=[d]
)
print(f"✅ Successfully indexed {len(documents)} documents!")
# User query
prompt = "What is python?"
print(f"\n❓ User Query: '{prompt}'")
print("-" * 40)
# Generate an embedding for the input and retrieve the most relevant doc
print("🔍 Searching knowledge base...")
response = ollama.embed(
model="mxbai-embed-large",
input=prompt
)
# Extract the first embedding and pass it correctly
query_embedding = response["embeddings"][0]
results = collection.query(
query_embeddings=[query_embedding],
n_results=1
)
# Get the most relevant document
data = results['documents'][0][0]
print(f"📄 Most relevant document found:")
print(f" → {data}")
# Generate a response combining the prompt and data we retrieved
print(f"\n🤖 Generating AI response using llama3.2...")
output = ollama.generate(
model="llama3.2",
prompt=f"Using this data: {data}. Respond to this prompt: {prompt}"
)
# Display the final response in a nice format with colors
print("\n" + Colors.CYAN + "=" * 80)
print("💬 AI RESPONSE")
print("=" * 80 + Colors.END)
print()
# Format the response with proper line breaks and indentation
response_text = output['response'].strip()
# Split into paragraphs for better readability
paragraphs = response_text.split('\n\n')
for paragraph in paragraphs:
if paragraph.strip():
# Wrap long lines for better readability
words = paragraph.strip().split()
line = ""
for word in words:
if len(line + word) > 75:
print(f"{Colors.GREEN} {line}{Colors.END}")
line = word + " "
else:
line += word + " "
if line.strip():
print(f"{Colors.GREEN} {line.strip()}{Colors.END}")
print()
print(Colors.CYAN + "=" * 80)
print("✨ RAG Process Complete!")
print("=" * 80 + Colors.END)
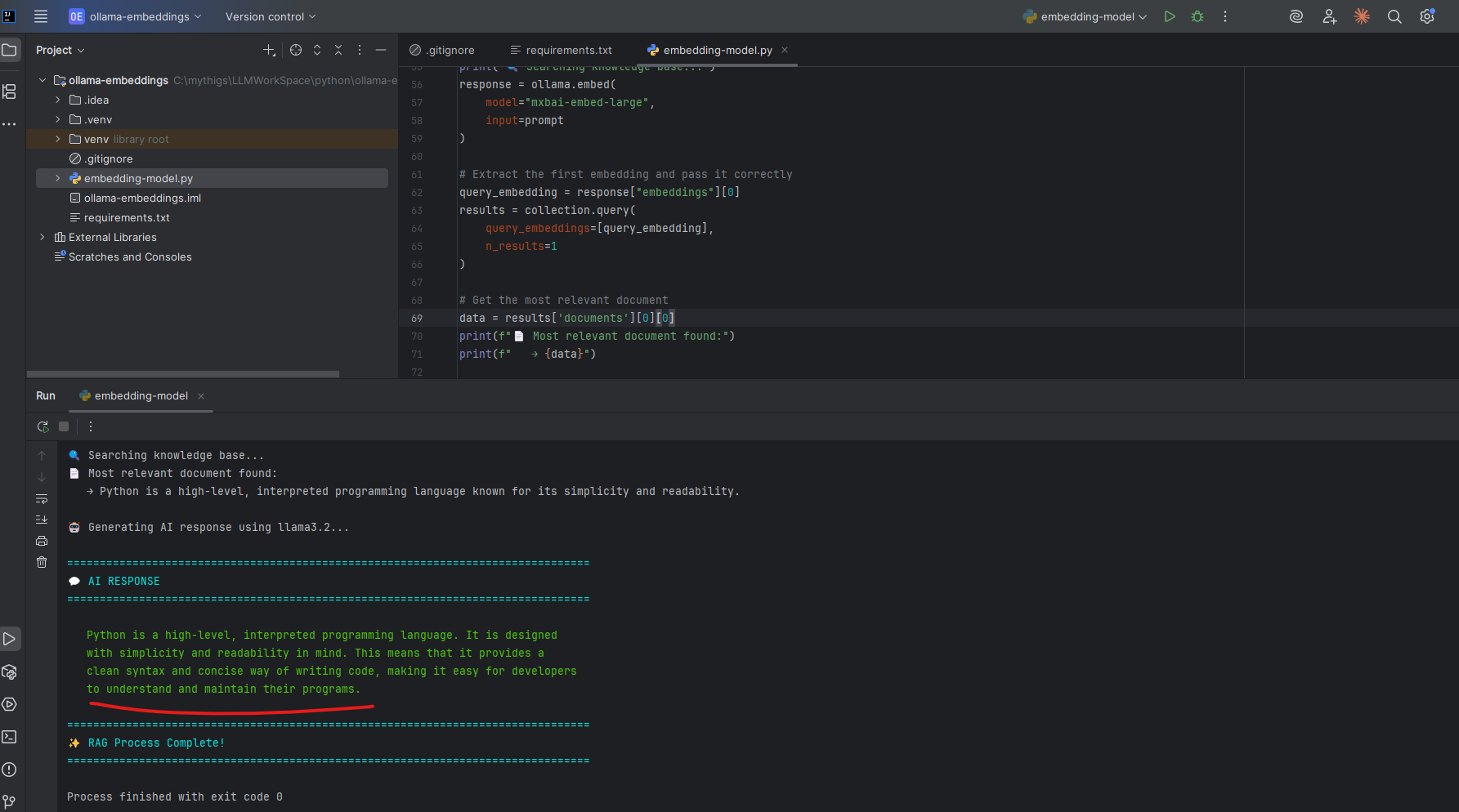
Running the Example
📁 Source Code Repository
🔗 GitHub Repository - Ollama Embeddings Example
Git Repository Setup
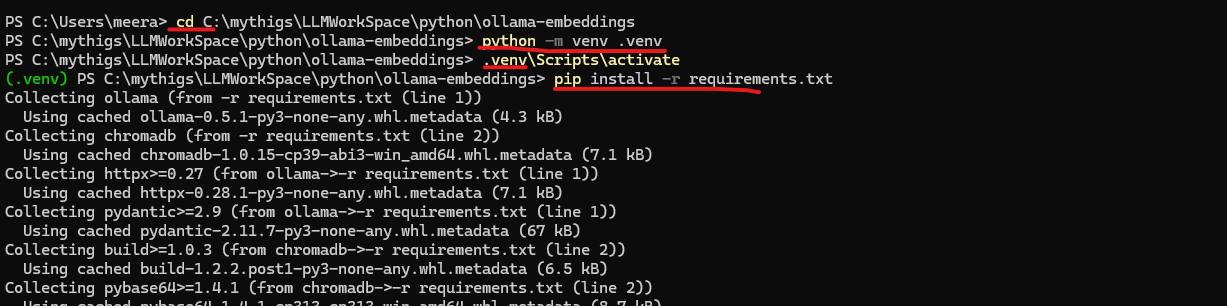
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/AI-Code-Geek/ollama-embeddings.git cd ollama-embeddings - Install Python virtual environment:
python3 -m venv .venv - Activate Python virtual environment:
# On Windows .venv\Scripts\activate # On macOS/Linux source .venv/bin/activate
- Install required Python packages:
pip install -r requirements.txt - Run the example:
python embedding-model.py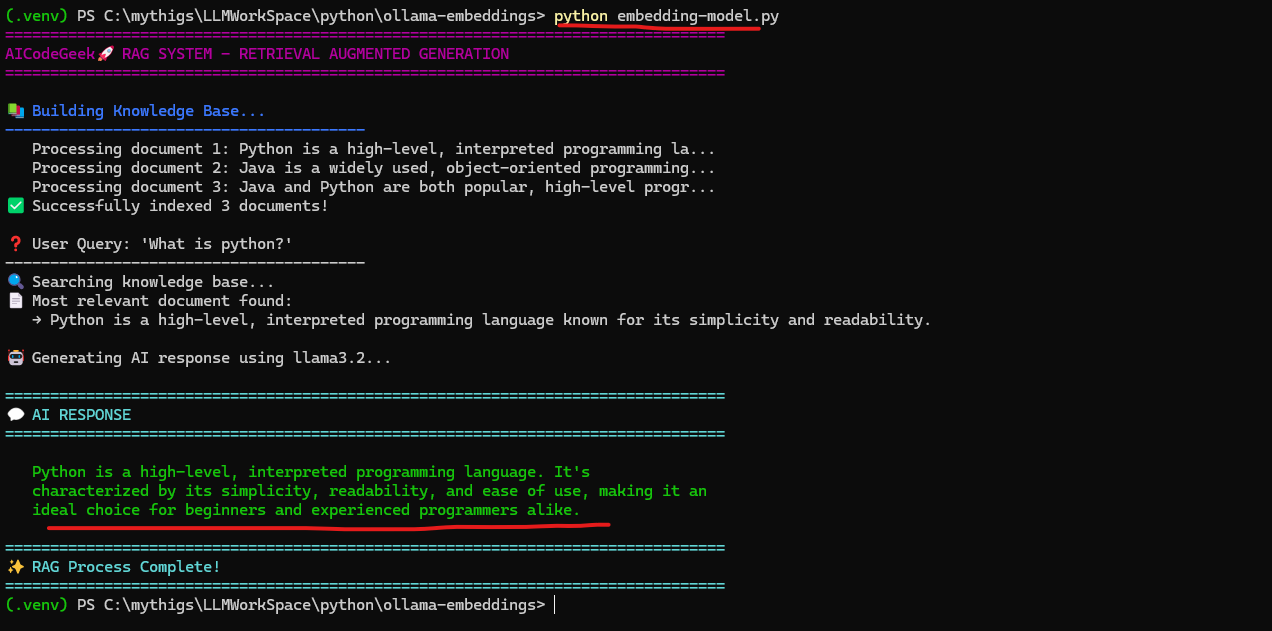
Intellij
🎉 Conclusion
This guide demonstrates how embedding models power intelligent RAG systems by transforming text into meaningful vector representations. By leveraging local models through Ollama, you can build privacy-focused, cost-effective RAG systems that provide accurate responses based on your specific knowledge base.
The combination of embedding models and vector databases creates a powerful foundation for building intelligent applications that can understand and retrieve contextually relevant information, making AI responses more accurate and domain-specific.
